In the realm of business operations, effective inventory management and stock control stand as cornerstones of success. By orchestrating these processes seamlessly, businesses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of business inventory management and stock control, exploring their significance, methodologies, and the transformative role of technology.
Throughout this discussion, we will uncover the various inventory management systems, unravel the complexities of stock control, and shed light on the importance of inventory optimization. Furthermore, we will delve into the realm of technology, examining its impact on inventory management and stock control practices.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is the process of managing the flow of goods and materials within a business. It involves tracking inventory levels, forecasting demand, and ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantity.
Effective inventory management is essential for businesses of all sizes. It can help to reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase profitability.
Types of Inventory Management Systems
There are a number of different inventory management systems available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Manual systemsare the most basic type of inventory management system. They involve tracking inventory levels manually, using spreadsheets or other tools.
- Automated systemsuse software to track inventory levels and automate tasks such as ordering and forecasting. They can be more efficient and accurate than manual systems, but they can also be more expensive.
- Hybrid systemscombine elements of both manual and automated systems. They can be a good option for businesses that need the flexibility of a manual system with the efficiency of an automated system.
Stock Control
Stock control is an integral part of inventory management that focuses on regulating the flow of goods within a warehouse or storage facility. It involves monitoring and managing inventory levels to ensure optimal stock availability while minimizing waste and costs.
Effective stock control helps businesses maintain the right balance of inventory, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking. It enables businesses to meet customer demand efficiently, prevent stockouts, and avoid the associated costs of excess inventory, such as storage, handling, and spoilage.
Methods and Techniques
Various methods and techniques are used for stock control, including:
- First-in, First-out (FIFO):This method assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold or used first, ensuring a regular flow of goods.
- Last-in, First-out (LIFO):This method assumes that the most recently acquired inventory items are sold or used first, potentially affecting the cost of goods sold during periods of price fluctuations.
- Periodic Inventory System:This method involves physically counting inventory at regular intervals to determine stock levels and adjust records accordingly.
- Perpetual Inventory System:This method continuously tracks inventory levels in real-time using software or other automated systems, providing up-to-date information on stock availability.
Challenges and Best Practices
Stock control presents several challenges, including:
- Inaccurate Inventory Records:Maintaining accurate inventory records is crucial for effective stock control. Inaccurate records can lead to stockouts or overstocking.
- Demand Forecasting:Predicting future demand accurately is essential for optimal stock levels. Inaccurate demand forecasts can result in stockouts or excess inventory.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:Unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or supplier delays, can disrupt the supply chain, affecting stock availability.
Best practices for effective stock control include:
- Establish Safety Stock Levels:Maintaining a buffer of safety stock helps mitigate the risk of stockouts during periods of high demand or supply chain disruptions.
- Implement Inventory Control Systems:Utilizing software or automated systems for inventory management can improve accuracy, efficiency, and real-time visibility.
- Monitor Inventory Regularly:Regularly reviewing inventory levels and identifying trends can help businesses make informed decisions about stock replenishment and demand forecasting.
Inventory Optimization: Business Inventory Management And Stock Control
Inventory optimization is crucial for businesses to streamline their supply chain, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. It involves finding the optimal balance between holding too much or too little inventory while meeting customer demand efficiently.
Approaches to Inventory Optimization
There are several approaches to inventory optimization, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:Aims to hold minimal inventory levels and receive materials or goods just before they are needed for production or sale.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ):Calculates the optimal quantity to order at a time to minimize total inventory costs, considering factors such as ordering costs and holding costs.
- Materials Requirement Planning (MRP):A comprehensive system that schedules production and inventory based on actual customer orders and forecasts, ensuring that the right materials are available when needed.
- Safety Stock:An additional inventory buffer held to mitigate the risk of stockouts due to unexpected demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions.
Examples of Inventory Optimization
Businesses can optimize their inventory through various methods:
- Utilizing inventory management software:Automates inventory tracking, reordering, and forecasting, providing real-time visibility and data for informed decision-making.
- Implementing a vendor-managed inventory (VMI) system:Allows suppliers to manage inventory levels on behalf of the business, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing overstocking or stockouts.
- Conducting regular inventory audits:Verifies inventory accuracy, identifies discrepancies, and helps prevent losses due to theft or spoilage.
- Establishing clear inventory policies and procedures:Defines roles, responsibilities, and guidelines for inventory management, ensuring consistency and efficiency.
Technology in Inventory Management and Stock Control
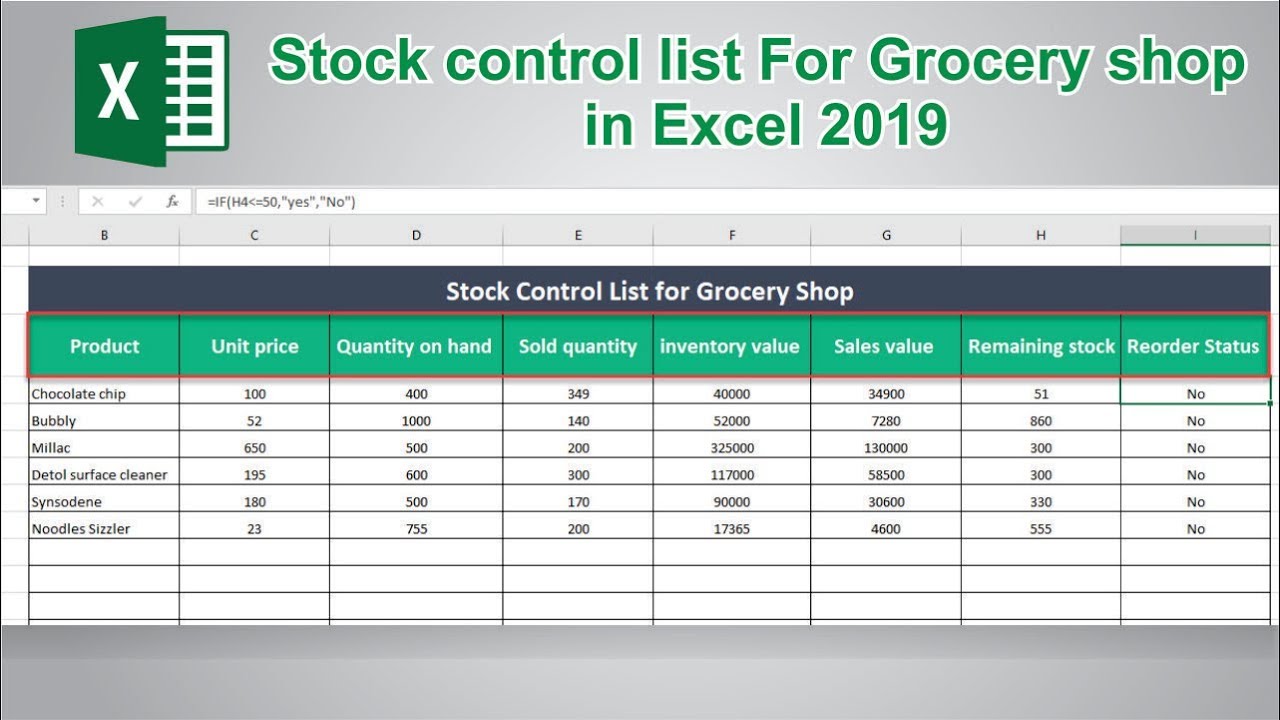
Technology plays a crucial role in modern inventory management and stock control, enabling businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve efficiency.
Software and Systems, Business inventory management and stock control
Various software and systems are available for inventory management, offering features such as:
- Real-time inventory tracking
- Automated reordering
- Inventory optimization
- Reporting and analytics
Benefits
Using technology in inventory management provides numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced inventory levels and carrying costs
- Improved customer service and reduced stockouts
- Enhanced forecasting and planning
- Increased visibility and control over inventory
Challenges
While technology offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges, such as:
- Cost of implementation and maintenance
- Data accuracy and integration with other systems
- Resistance to change and training requirements
Case Studies and Examples

Businesses of all sizes can benefit from implementing effective inventory management and stock control systems. Here are a few case studies and examples to illustrate the positive impact these systems can have on operations:
Case Study: Amazon
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, has implemented a sophisticated inventory management system that enables it to track inventory levels in real-time across its vast network of warehouses. This system helps Amazon to optimize its inventory levels, reduce waste, and improve customer service by ensuring that products are always in stock and available for purchase.
Case Study: Toyota
Toyota, the Japanese automaker, uses a just-in-time inventory management system to minimize inventory levels and reduce waste. This system involves producing only the parts and materials that are needed for immediate production, which helps Toyota to save on storage costs and improve efficiency.
Challenges in Implementing Inventory Management Systems
While inventory management and stock control systems can provide significant benefits, there are also some challenges that businesses may face when implementing these systems:
- Cost:Implementing an inventory management system can be expensive, especially for businesses with large or complex inventory operations.
- Complexity:Inventory management systems can be complex to implement and manage, especially for businesses with a large number of products or locations.
- Data accuracy:Maintaining accurate inventory data is essential for effective inventory management. However, this can be challenging for businesses with a large or rapidly changing inventory.
Outcome Summary

As we conclude our exploration of business inventory management and stock control, it is evident that these practices are indispensable for businesses seeking to streamline their operations, minimize waste, and maximize profitability. By embracing effective inventory management and stock control strategies, businesses can gain a competitive edge, respond swiftly to market demands, and ultimately achieve operational excellence.
Quick FAQs
What is the primary objective of inventory management?
Inventory management aims to maintain optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs associated with holding excess inventory.
How does stock control contribute to inventory management?
Stock control ensures that inventory records are accurate and up-to-date, enabling businesses to track inventory levels, identify discrepancies, and prevent stockouts.
What are the benefits of implementing an inventory management system?
Inventory management systems automate inventory tracking, streamline ordering processes, and provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, leading to improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer service.