Business inventory meaning delves into the heart of inventory management, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance in driving business operations. Inventory, the lifeblood of any enterprise, encompasses raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, forming the foundation for efficient production and seamless customer fulfillment.
Inventory management techniques empower businesses to optimize their inventory levels, ensuring availability while minimizing waste. From inventory management software to robust inventory control systems, businesses can leverage a range of tools to maintain accurate inventory records, prevent shrinkage, and streamline operations.
Business Inventory Definition
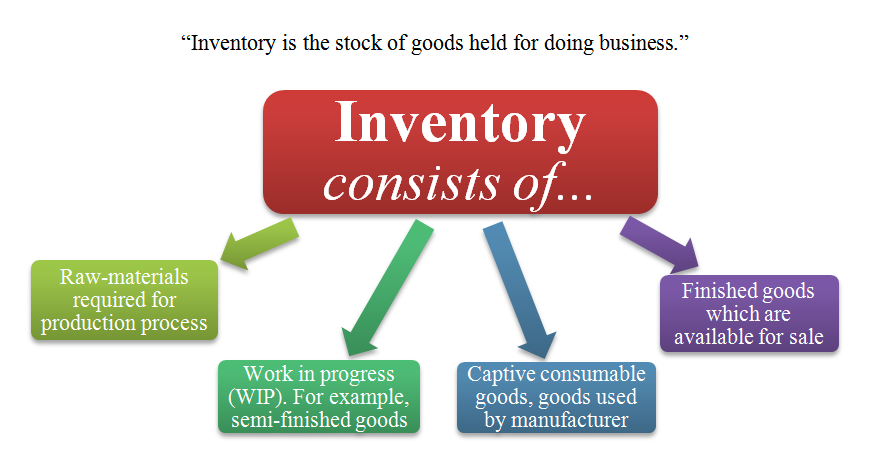
Business inventory refers to the physical goods or merchandise that a company holds for sale to its customers. It includes all items that are part of the production process, from raw materials to finished goods ready for sale.
Inventory is an essential component of any business, as it represents the products that generate revenue. Managing inventory effectively is crucial for ensuring that a business has the right products, in the right quantities, at the right time to meet customer demand.
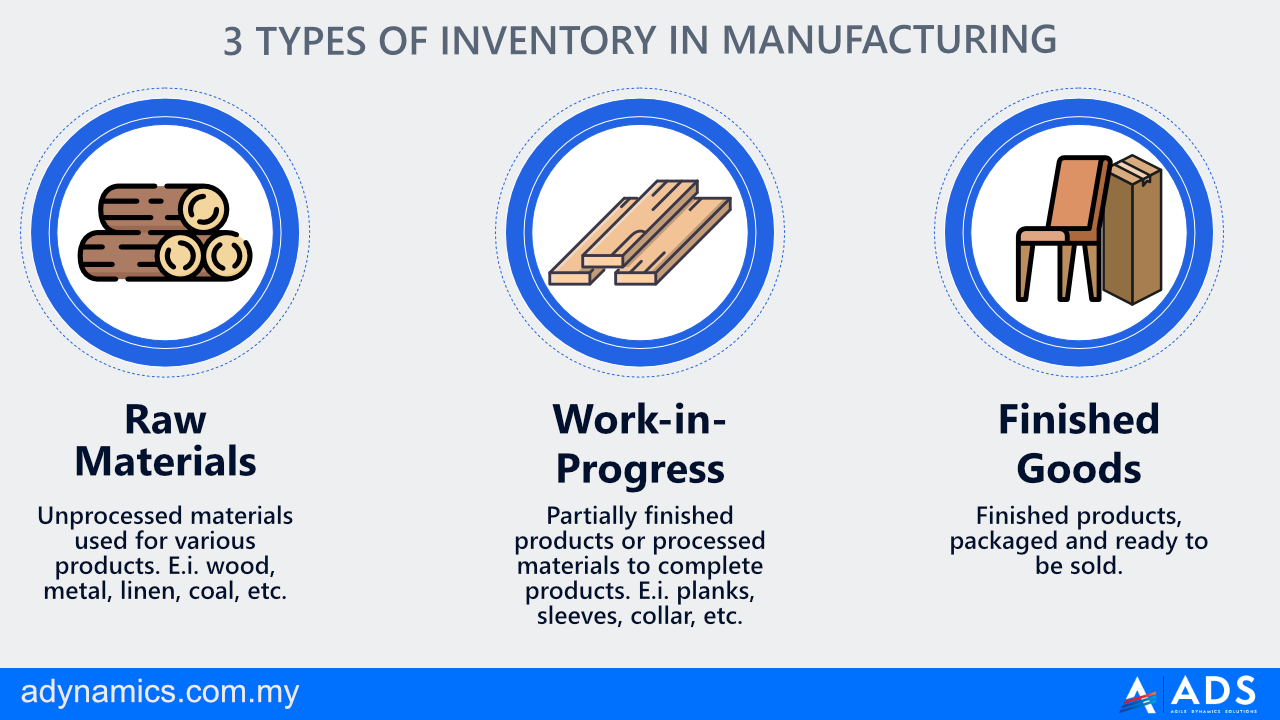
Types of Inventory
There are various types of inventory, each serving a specific purpose in the production and sales process:
- Raw materials:These are the basic components used to create finished goods. Examples include wood for furniture, fabric for clothing, and ingredients for food products.
- Work-in-progress (WIP):This refers to goods that are partially completed but not yet ready for sale. WIP inventory includes items that are undergoing manufacturing or assembly processes.
- Finished goods:These are products that are complete and ready to be sold to customers. Finished goods inventory represents the products that a business has available for sale.
Inventory Management Techniques
Effective inventory management techniques enable businesses to optimize stock levels, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Here are some key strategies:
Businesses can implement various inventory management techniques to enhance their operations. These techniques help businesses optimize stock levels, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Let’s explore some effective strategies:
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory
- JIT aims to minimize inventory by ordering products only when needed, reducing storage costs and the risk of obsolescence.
- Example: Toyota’s Kanban system uses visual cues to signal when to replenish inventory.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
- FIFO ensures that the oldest inventory is sold first, preventing spoilage and obsolescence.
- Example: Grocers use FIFO to manage perishable items like produce and dairy products.
Inventory Management Software and Tools, Business inventory meaning
Inventory management software and tools automate inventory tracking, optimize ordering, and provide real-time data:
- Example:QuickBooks, SAP, NetSuite
Benefits of Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances customer service:
- Reduced carrying costs:Lower storage, insurance, and handling expenses.
- Improved cash flow:Optimized inventory levels free up capital for other business activities.
- Increased customer satisfaction:Reduced stockouts and faster order fulfillment.
Inventory Valuation Methods
Inventory valuation is the process of assigning a monetary value to the inventory on hand. There are a number of different methods that can be used to value inventory, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common inventory valuation methods are:
- First-in, first-out (FIFO)
- Last-in, first-out (LIFO)
- Weighted average cost
FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first. This means that the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the oldest inventory on hand. LIFO assumes that the newest inventory is sold first. This means that the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the newest inventory on hand.
Weighted average cost assumes that all of the inventory on hand is sold at the same time. This means that the cost of goods sold is based on the average cost of all of the inventory on hand.
The choice of which inventory valuation method to use depends on a number of factors, including the nature of the business, the inventory turnover rate, and the tax implications. FIFO is generally preferred when inventory turnover is high and prices are rising.
LIFO is generally preferred when inventory turnover is low and prices are falling. Weighted average cost is generally preferred when inventory turnover is moderate and prices are stable.
Inventory valuation has a significant impact on financial statements. The choice of inventory valuation method can affect the reported cost of goods sold, net income, and ending inventory. It can also affect the company’s tax liability.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FIFO
- Advantages:
- FIFO provides the most accurate measure of current inventory costs.
- FIFO is easy to implement and understand.
- FIFO is generally accepted by the IRS.
- Disadvantages:
- FIFO can result in a mismatch between the physical flow of inventory and the cost of goods sold.
- FIFO can lead to higher reported profits during periods of rising prices.
- FIFO can lead to lower reported profits during periods of falling prices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LIFO
- Advantages:
- LIFO provides the most accurate measure of current inventory costs during periods of rising prices.
- LIFO can lead to lower reported profits during periods of rising prices.
- LIFO can lead to higher reported profits during periods of falling prices.
- Disadvantages:
- LIFO can result in a mismatch between the physical flow of inventory and the cost of goods sold.
- LIFO is more complex to implement and understand than FIFO.
- LIFO is not generally accepted by the IRS.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Weighted Average Cost
- Advantages:
- Weighted average cost provides a more stable measure of inventory costs than FIFO or LIFO.
- Weighted average cost is easier to implement and understand than LIFO.
- Weighted average cost is generally accepted by the IRS.
- Disadvantages:
- Weighted average cost does not provide as accurate a measure of current inventory costs as FIFO or LIFO.
- Weighted average cost can lead to a mismatch between the physical flow of inventory and the cost of goods sold.
Inventory Control
Inventory control is a critical aspect of inventory management that helps businesses maintain accurate inventory levels, prevent shrinkage and theft, and ensure efficient tracking and monitoring of inventory items.Inventory control systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing businesses to make informed decisions about replenishment, production, and sales.
Effective inventory control practices can help businesses reduce carrying costs, improve customer service, and optimize cash flow.
Preventing Inventory Shrinkage and Theft
Inventory shrinkage refers to the loss of inventory due to factors such as theft, damage, or obsolescence. Preventing inventory shrinkage is essential for maintaining accurate inventory levels and maximizing profitability.Businesses can implement various measures to prevent inventory shrinkage, including:
- Implementing physical security measures such as surveillance cameras, access control systems, and alarms.
- Establishing clear inventory policies and procedures, including regular inventory counts and cycle counting.
- Training employees on inventory management best practices and security protocols.
- Partnering with reliable suppliers to ensure the quality and accuracy of incoming inventory.
Best Practices for Inventory Tracking and Monitoring
Effective inventory tracking and monitoring are crucial for maintaining accurate inventory records and ensuring efficient inventory management. Businesses can adopt various best practices to improve their inventory tracking and monitoring processes:
- Regular inventory counts:Conducting regular physical inventory counts helps identify discrepancies between actual and recorded inventory levels, allowing businesses to address shrinkage and ensure accuracy.
- Cycle counting:Cycle counting involves counting a portion of inventory items on a regular basis, rather than counting the entire inventory at once. This helps identify discrepancies and errors in a timely manner.
- Automated inventory management systems:Using automated inventory management systems can streamline inventory tracking and monitoring processes, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
- Barcode and RFID technology:Implementing barcode or RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology can facilitate accurate and efficient inventory tracking by automating data collection and reducing the risk of errors.
Inventory Analysis: Business Inventory Meaning
Inventory analysis involves examining a company’s inventory levels, patterns, and related costs to optimize inventory management and improve overall business operations.
Inventory analysis helps businesses understand their inventory performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions regarding inventory levels, storage, and replenishment strategies.
Key Inventory Metrics
- Inventory Turnover Ratio:Measures how efficiently a company is managing its inventory. A higher ratio indicates faster inventory turnover and better inventory management.
- Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO):Indicates the average number of days that inventory is held before it is sold. A lower DIO indicates more efficient inventory management.
- Inventory Holding Cost:Represents the cost of storing and maintaining inventory, including storage space, insurance, and handling expenses.
- Inventory Carrying Cost:Includes the inventory holding cost plus the opportunity cost of capital invested in inventory.
Benefits of Inventory Analysis
- Improved inventory management
- Reduced inventory costs
- Enhanced customer service
- Increased profitability
- Better decision-making
Inventory Optimization

Inventory optimization is the process of managing inventory levels to minimize costs while ensuring that customer demand is met. It involves balancing the trade-off between holding too much inventory, which can lead to high storage costs and obsolescence, and holding too little inventory, which can result in stockouts and lost sales.
There are a number of different inventory optimization strategies that can be used, depending on the specific needs of a business. Some of the most common strategies include:
- Just-in-time (JIT) inventory:JIT is a strategy that aims to minimize inventory levels by only ordering inventory when it is needed. This can help to reduce storage costs and obsolescence, but it requires a high level of coordination with suppliers.
- Economic order quantity (EOQ):EOQ is a formula that can be used to determine the optimal quantity of inventory to order at a time. EOQ takes into account factors such as the cost of ordering, the cost of holding inventory, and the demand for the product.
- Safety stock:Safety stock is a buffer of inventory that is held to protect against unexpected changes in demand or supply. Safety stock can help to prevent stockouts, but it also increases inventory costs.
Factors to Consider When Developing an Inventory Optimization Plan
When developing an inventory optimization plan, it is important to consider a number of factors, including:
- The nature of the business
- The products being sold
- The demand for the products
- The cost of ordering and holding inventory
- The level of customer service that is desired
Case Studies of Businesses that Have Successfully Implemented Inventory Optimization Techniques
There are a number of businesses that have successfully implemented inventory optimization techniques. Some of these businesses include:
- Amazon:Amazon uses a variety of inventory optimization techniques, including JIT and EOQ, to manage its vast inventory.
- Walmart:Walmart uses a cross-docking strategy to reduce inventory levels and improve efficiency.
- Toyota:Toyota uses a JIT strategy to minimize inventory levels and improve production efficiency.
Inventory Financing
Inventory financing is a financial tool that businesses can use to finance their inventory. This can be a helpful way to free up cash flow and support business growth. There are a variety of different inventory financing methods available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Types of Inventory Financing
One common type of inventory financing is a line of credit. This is a revolving loan that allows businesses to borrow money up to a certain limit. Lines of credit are typically used to finance short-term inventory needs, such as seasonal fluctuations in demand.Another type of inventory financing is a purchase order financing.
This type of financing is used to finance the purchase of specific inventory items. Purchase order financing is typically used by businesses that have large, one-time inventory purchases.Finally, there is also factoring. Factoring is a type of inventory financing in which a business sells its accounts receivable to a factoring company.
The factoring company then advances the business a percentage of the value of the accounts receivable. Factoring can be a helpful way to free up cash flow and improve liquidity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Inventory Financing
There are a number of advantages to using inventory financing. First, it can help businesses to free up cash flow. This can be helpful for businesses that are experiencing seasonal fluctuations in demand or that have large, one-time inventory purchases.
Second, inventory financing can help businesses to improve their liquidity. This can be helpful for businesses that need to meet short-term financial obligations. Third, inventory financing can help businesses to support their growth. By providing businesses with the financial resources they need to purchase inventory, inventory financing can help them to grow their sales and profits.However, there are also some disadvantages to using inventory financing.
First, it can be expensive. Interest rates on inventory financing can be higher than interest rates on other types of loans. Second, inventory financing can be risky. If the value of the inventory declines, the business may be left with a loss.
Third, inventory financing can be complex. The terms and conditions of inventory financing can be complex and difficult to understand.
How Inventory Financing Can Support Business Growth
Inventory financing can support business growth in a number of ways. First, it can help businesses to free up cash flow. This can be helpful for businesses that are experiencing seasonal fluctuations in demand or that have large, one-time inventory purchases.
By freeing up cash flow, inventory financing can help businesses to invest in other areas of their business, such as marketing and sales.Second, inventory financing can help businesses to improve their liquidity. This can be helpful for businesses that need to meet short-term financial obligations.
By improving liquidity, inventory financing can help businesses to avoid financial distress and bankruptcy.Third, inventory financing can help businesses to support their growth. By providing businesses with the financial resources they need to purchase inventory, inventory financing can help them to grow their sales and profits.
Inventory financing can be a valuable tool for businesses that are looking to grow their business.
Closing Summary

In conclusion, business inventory meaning underscores the critical role of inventory in business success. Effective inventory management strategies enable businesses to optimize stock levels, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. By embracing inventory analysis, businesses gain valuable insights into their inventory performance, driving informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
FAQ
What is the purpose of inventory management?
Inventory management aims to maintain optimal inventory levels, ensuring availability for production and sales while minimizing waste and storage costs.
What are the key inventory management techniques?
Effective inventory management techniques include implementing inventory management software, utilizing inventory control systems, and conducting regular inventory audits.
How does inventory valuation impact financial statements?
Inventory valuation methods, such as FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average cost, directly affect the value of inventory reported on financial statements, impacting profitability and asset valuation.