Business inventory policies lay the groundwork for efficient inventory management, ensuring businesses maintain optimal stock levels, minimize costs, and maximize profitability. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of inventory management, providing insights into its importance, various types of inventory, and effective control techniques.
Understanding inventory management is crucial for businesses of all sizes. It helps them avoid stockouts, reduce waste, and optimize cash flow. Effective inventory policies serve as a roadmap, guiding businesses towards efficient inventory practices that align with their unique needs and industry-specific challenges.
Inventory Management Fundamentals: Business Inventory Policies
Inventory management is the process of controlling the flow of goods through a business. It involves activities such as purchasing, storing, and distributing inventory. Effective inventory management is essential for businesses of all sizes, as it can help to reduce costs, improve customer service, and increase profitability.
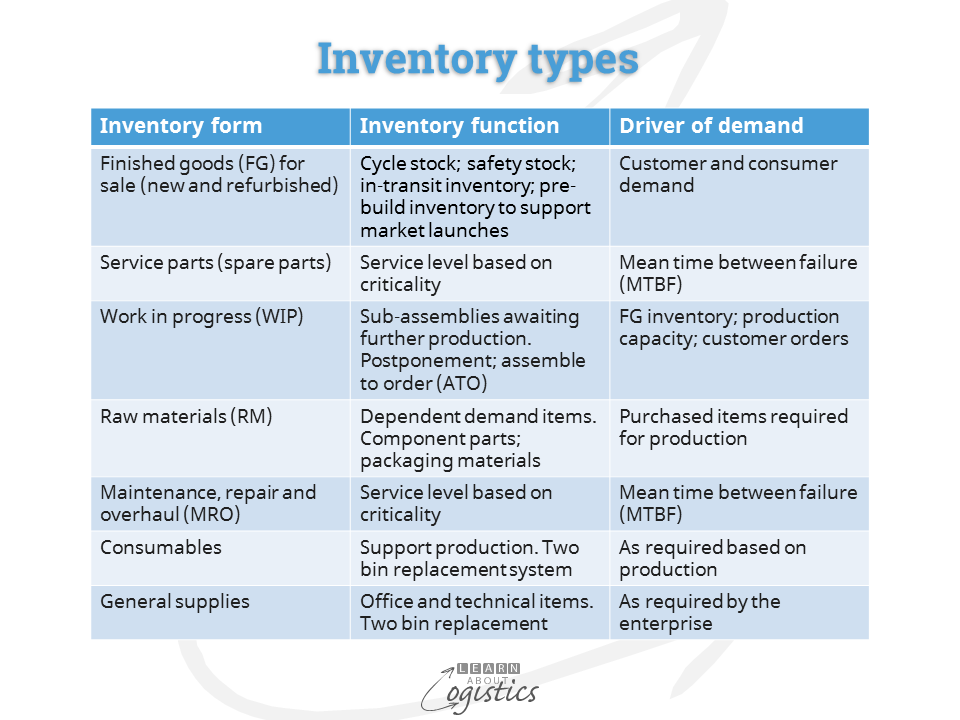
There are several different types of inventory, including:
- Raw materials:These are the basic materials used to produce finished goods.
- Work-in-process inventory:These are goods that are in the process of being produced.
- Finished goods:These are goods that are ready to be sold to customers.
- Maintenance, repair, and operating (MRO) supplies:These are items that are used to maintain and repair equipment and facilities.
Inventory Control Techniques

Inventory control techniques are methods used to manage and optimize inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing costs. These techniques include ABC analysis, inventory valuation methods, and inventory control systems.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is a method of inventory classification that groups inventory items into three categories based on their annual usage value. Category A items are the most valuable and represent the highest percentage of total inventory value. Category B items have a moderate usage value, while Category C items have the lowest usage value.
ABC analysis helps businesses prioritize inventory management efforts by focusing on the most critical items (Category A) and reducing the risk of stockouts for these items.
Inventory Valuation Methods
Inventory valuation methods are used to determine the cost of inventory for financial reporting purposes. The two most common inventory valuation methods are:
- FIFO (First-In, First-Out):This method assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first. As a result, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the oldest inventory items.
- LIFO (Last-In, First-Out):This method assumes that the newest inventory items are sold first. As a result, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the newest inventory items.
The choice of inventory valuation method can impact the reported profitability and financial position of a business.
Inventory Control Systems
Inventory control systems are software applications that help businesses manage their inventory levels. These systems can track inventory items, record transactions, and generate reports. Inventory control systems can help businesses improve inventory accuracy, reduce stockouts, and optimize inventory levels.
Inventory Optimization Strategies
Optimizing inventory levels is crucial for maintaining a lean and efficient supply chain. By striking the right balance between stock availability and holding costs, businesses can maximize profits and customer satisfaction.
One key aspect of inventory optimization is determining the appropriate safety stock levels. Safety stock serves as a buffer against unexpected fluctuations in demand or supply disruptions. Maintaining adequate safety stock helps prevent stockouts and ensures uninterrupted operations.
Just-in-Time Inventory Management, Business inventory policies
Just-in-time (JIT) inventory management is a strategy that aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when they are needed for production or sale. JIT helps reduce holding costs, improve cash flow, and enhance responsiveness to changes in demand.
However, it requires close coordination with suppliers and efficient logistics systems.
- Benefits of JIT Inventory Management:
- Reduced inventory holding costs
- Improved cash flow
- Enhanced flexibility and responsiveness to demand changes
- Minimized waste and obsolescence
Inventory Costing Methods
Inventory costing methods are used to determine the cost of inventory items for financial reporting purposes. The choice of inventory costing method can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements.There are several different inventory costing methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common inventory costing methods are:
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
Under FIFO, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the oldest inventory items. This method assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first. FIFO can result in higher cost of goods sold and lower net income in periods of rising prices.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
Under LIFO, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the most recent inventory items. This method assumes that the most recent inventory items are sold first. LIFO can result in lower cost of goods sold and higher net income in periods of rising prices.
Weighted Average Cost
Under weighted average cost, the cost of goods sold is based on the average cost of all inventory items. This method is less sensitive to changes in inventory costs than FIFO or LIFO.The choice of inventory costing method should be based on the company’s specific circumstances.
Factors to consider include the nature of the inventory, the rate of inventory turnover, and the company’s accounting policies.
Inventory Valuation Methods

Inventory valuation is the process of determining the value of inventory on hand at a specific point in time. Inventory costing, on the other hand, is the process of assigning costs to inventory items. While inventory valuation and inventory costing are related, they are not the same thing.
There are a number of different inventory valuation methods that can be used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common inventory valuation methods include:
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
- Under FIFO, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the oldest inventory items on hand.
- This method assumes that the oldest inventory items are the first to be sold.
- FIFO can result in a higher cost of goods sold during periods of rising prices, and a lower cost of goods sold during periods of falling prices.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
- Under LIFO, the cost of goods sold is based on the cost of the newest inventory items on hand.
- This method assumes that the newest inventory items are the first to be sold.
- LIFO can result in a lower cost of goods sold during periods of rising prices, and a higher cost of goods sold during periods of falling prices.
Weighted Average Cost
- Under weighted average cost, the cost of goods sold is based on the average cost of all inventory items on hand.
- This method is less sensitive to changes in inventory prices than FIFO or LIFO.
- Weighted average cost can result in a more stable cost of goods sold over time.
Specific Identification
- Under specific identification, each inventory item is tracked individually and its cost is assigned to the item.
- This method is the most accurate, but it can also be the most time-consuming.
- Specific identification is often used for high-value inventory items.
The choice of inventory valuation method can have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements. For example, a company that uses FIFO will report a higher cost of goods sold and a lower net income during periods of rising prices than a company that uses LIFO.
This is because FIFO assumes that the oldest inventory items are the first to be sold, which means that the cost of goods sold will be based on the lower prices of the older inventory items.
It is important to choose an inventory valuation method that is appropriate for the company’s business and that will provide accurate and reliable financial information.
Inventory Performance Measurement
Inventory performance measurement is crucial for businesses to assess the effectiveness of their inventory management practices and identify areas for improvement. Key metrics used to measure inventory performance include:* Inventory Turnover:Measures how quickly inventory is sold and replaced.
Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO)
Indicates the average number of days inventory is held before being sold.
Inventory Accuracy
Assesses the accuracy of inventory records compared to physical inventory counts.
Stockout Rate
Measures the percentage of customer orders that cannot be fulfilled due to stockouts.
Obsolescence Rate
Calculates the percentage of inventory that becomes obsolete or unsalable over a period.These metrics provide valuable insights into inventory management practices, such as the efficiency of inventory replenishment, the effectiveness of inventory planning, and the accuracy of inventory records.
Inventory Turnover
Inventory turnover is a critical metric that reflects the rate at which inventory is converted into sales. A high inventory turnover indicates that the business is effectively managing its inventory, minimizing holding costs, and meeting customer demand efficiently. Conversely, a low inventory turnover suggests inefficiencies in inventory management, leading to increased storage costs, obsolescence, and potential stockouts.To improve inventory turnover, businesses can implement strategies such as:* Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Management:Minimizes inventory levels by receiving goods only when needed for production or sale.
Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)
Allows suppliers to manage inventory levels on behalf of the business, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing overstocking.
Safety Stock Optimization
Determining the optimal level of safety stock to minimize the risk of stockouts while avoiding excessive inventory holding costs.
Inventory Management in Different Industries
Inventory management practices vary across industries due to unique challenges and requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing inventory management strategies and achieving operational efficiency.
Retail Industry
- High product variety and rapid turnover rates.
- Emphasis on customer service and quick order fulfillment.
- Best Practices:
- Implement perpetual inventory systems for real-time tracking.
- Utilize RFID technology for efficient stocktaking and product identification.
- Adopt just-in-time inventory strategies to minimize holding costs.
Manufacturing Industry
- Complex production processes with multiple components.
- Need for raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods inventory.
- Best Practices:
- Use material requirements planning (MRP) systems to forecast demand and optimize production schedules.
- Implement kanban systems for efficient flow of materials within production lines.
- Conduct regular cycle counting to ensure inventory accuracy.
Healthcare Industry
- Life-saving products with strict quality and safety regulations.
- High demand for specialized medical supplies and equipment.
- Best Practices:
- Establish a comprehensive inventory management system to track medical supplies, equipment, and pharmaceuticals.
- Implement barcode scanning and RFID technology for accurate and efficient inventory control.
- Maintain safety stock levels to prevent shortages and ensure patient care.
Impact of Technology on Inventory Management
Technological advancements have significantly impacted inventory management across industries:
- Data Analytics:Real-time data collection and analysis enable businesses to forecast demand more accurately, optimize inventory levels, and identify trends.
- Cloud Computing:Cloud-based inventory management systems provide remote access, scalability, and enhanced collaboration.
- Internet of Things (IoT):IoT devices connected to inventory items provide real-time visibility, automate inventory tracking, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Inventory Management Trends and Best Practices
Inventory management practices are constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer demands. Staying abreast of these trends and implementing best practices can significantly improve inventory efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Emerging Trends in Inventory Management
- Real-time Visibility and Analytics:Advanced technologies like IoT sensors and data analytics provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing businesses to make informed decisions based on accurate data.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):AI and ML algorithms can automate inventory forecasting, optimize replenishment strategies, and identify patterns in demand.
- Cloud-based Inventory Management Systems:Cloud-based systems offer scalability, accessibility, and integration with other business applications, enhancing collaboration and data sharing.
- Collaborative Inventory Planning:Businesses are increasingly collaborating with suppliers and customers to share data and improve inventory visibility throughout the supply chain.
- Sustainability and Environmental Considerations:Growing awareness of environmental impact is driving businesses to implement sustainable inventory practices, such as reducing waste and optimizing packaging.
Tips for Implementing Best Practices in Inventory Management
- Establish Clear Inventory Policies and Procedures:Define clear guidelines for inventory management, including inventory levels, reorder points, and safety stock.
- Implement Inventory Tracking Systems:Use technology to track inventory levels, monitor stock movements, and generate reports for analysis.
- Optimize Inventory Levels:Determine optimal inventory levels based on demand patterns, lead times, and safety stock requirements.
- Implement Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory:JIT aims to minimize inventory levels by receiving goods only when they are needed, reducing storage costs and improving cash flow.
- Monitor Inventory Performance:Regularly track inventory turnover, stockout rates, and other metrics to identify areas for improvement.
Role of Technology in Improving Inventory Management
Technology plays a crucial role in improving inventory management efficiency. Advanced systems and tools can automate processes, provide real-time visibility, and enable data-driven decision-making.
- Inventory Management Software:Dedicated software can streamline inventory processes, automate replenishment, and provide comprehensive reporting.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS):WMS helps optimize warehouse operations, including inventory tracking, picking, and packing.
- RFID and Barcode Scanning:These technologies automate inventory tracking, reducing errors and improving accuracy.
- Cloud-based Inventory Management:Cloud-based systems offer real-time data access, collaboration, and scalability.
- Predictive Analytics:AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical data and forecast future demand, enabling businesses to optimize inventory levels.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, business inventory policies are a cornerstone of successful inventory management. By implementing sound policies and leveraging effective control techniques, businesses can optimize inventory levels, minimize costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Embracing best practices and staying abreast of emerging trends in inventory management empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of supply chain management and achieve sustainable growth.
Questions Often Asked
What are the key elements of business inventory policies?
Business inventory policies typically include guidelines for inventory levels, reorder points, safety stock, inventory valuation methods, and inventory control techniques.
How do businesses determine optimal inventory levels?
Businesses can use various techniques to determine optimal inventory levels, such as ABC analysis, safety stock calculations, and just-in-time inventory management principles.
What are the advantages of implementing effective inventory control systems?
Effective inventory control systems help businesses maintain accurate inventory records, reduce shrinkage, improve inventory turnover, and enhance overall inventory management efficiency.